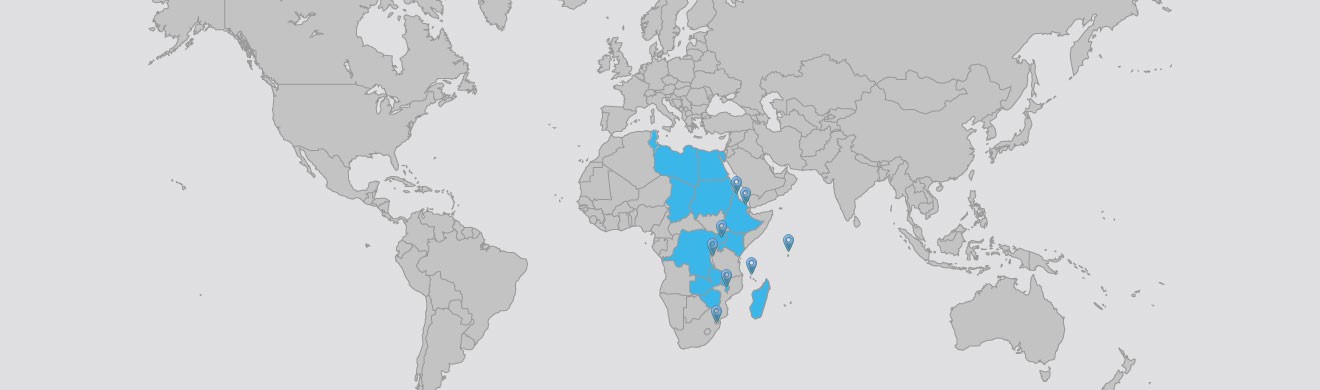
Common Market for Southern and Eastern Africa (COMESA)
The COMESA Free Trade Area (FTA) was launched on 31 October 2000 with nine Member States. This was the first FTA in Africa under the African Union. The FTA consists of 16 Member States trading on a full duty free and quota free basis, with the remaining countries at various stages of joining the FTA.
Member States
- COMESA FTA Member States : Burundi, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Rwanda, Seychelles, Sudan, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
- COMESA NON FTA Member States : Democratic Republic of Congo, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Swaziland.
The COMESA Treaty
Exporting to COMESA Countries
Duty Free Access to COMESA Member States : To benefit from duty free access in the COMESA region, an exporter must consign his products to countries belonging to the FTA. FTA countries, also known as Group 1 Member States trade on a duty free, quota free basis.
Rules of Origin: The exporter must also ensure that his products satisfy the Rules of Origin. Complete information on the Rules of Origin is available in the COMESA Procedures Manual on the Implementation of the Protocol on the Rules of Origin.
Products shall be considered and accepted as having COMESA preferential origin if they have undergone the following:
- The goods have been wholly produced or obtained in the COMESA Member State; or
- The goods have been produced in the COMESA Member State and the CIF value of any imported raw materials used in their production should not exceed 60% of the total cost of all materials used in their production; or
- The value added resulting from the process of producing the goods from imported materials should account for at least 35% of the ex-factory cost of the goods; or
- The goods should be produced in a Member State and be classified or become classified, after the process of production, under a tariff heading other than the tariff heading under which they were imported (CTH rule). For the list of products for which the CTH rule has been agreed, click here.
Obtaining a COMESA Certificate of Origin : The COMESA Certificate of Origin is issued and approved by:
Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Consumer Protection
Trade Division
4th Floor, Anglo-Mauritius Building
Intendance Street
Port-Louis
Tel: (230) 405 1399
Fax: (230) 208 7325
Email: td@mail.govmu.org
Website: industry.govmu.org
The documents required for approval are as follows:
1. Duly filled COMESA Certificate of Origin
2. Customs Declaration (Import and Export)
3. Export Invoice
4. Appropriate Certified Costing for value added requirements
5. Export Permit (if applicable)
6. Any other documents that may be required
Importing from COMESA Countries
All imports entering Mauritius from a COMESA Group I Member State with a valid Certificate of Origin are completely exempt from customs duties.
A 90% tariff reduction is applicable to imports from non-FTA COMESA countries (also known as Group II Member States) with a valid Certificate of Origin.
The COMESA Regional and Electronic Payment and Settlement System (REPSS)
Member countries can transfer funds more easily within COMESA with REPSS. Importers can pay for goods and services in their local currencies, whilst exporters will be able to invoice their products in their local currency. REPSS is built on open standards and is also accessible to non-member states.
As at January 2015, REPSS counted 6 live participants, namely, Malawi, Swaziland, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya and Mauritius.
Local banks can access the payment system through their Central Banks. For more information on COMESA REPSS, click here.
Reporting Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs)
NTBs refer to restrictions that result from prohibitions, conditions, or specific market requirements that make importation or exportation of products difficult and/or costly.
Operators can directly report any barriers to trade encountered in the COMESA region through the Non-Tariff Trade Barriers Website. The system also allows for monitoring of the resolution of the complaint filed.
More information can be obtained on the Non-Tariff Trade Barriers Website or the MCCI which is the national private sector focal point for assisting the business community in the reporting process.
Useful Links
Australia
June 1995
Australian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (ACCI)
Austria
September 2014
Austrian Federal Economic Chamber
China
April 1997
China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT) - Beijing
China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission - Shanghai
November 1998
CCPIT Guangdong Sub-Council
September 2008
CCPIT Qingdao
May 2007
CCPIT Qingdao
Comores
April 2017
L´Union des Chambres de Commerce, d´Industrie et d´Agriculture
Djibouti
August 2008
Chamber of Commerce of Djibouti
Estonia
September 2015
Estonia Chamber of Commerce and Industry
France
September 1996
l’Assemblée des Chambres Françaises de Commerce et d’Industrie (ACFCI)
India
November 1985
Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI)
May 1996
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII)
June 1995
Tamil Nadu Chamber of Commerce and Industry
January 2004
India International Trade Center
May 2004
Seafood Exporters Association of India
October 2005
Seafood Exporters Association of India
Kenya
January 2011
The Kenya National Chamber of Commerce and Industry (KNCCI)
Madagascar
November 2004
Fédération des Chambres de Commerce, d’Industrie, d’Artisanat et d’Agriculture de Madagascar
Malaysia
August 1994
The National Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Malaysia
June 2005
Malaysian Associated Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry
Mozambique
September 2012
Chamber of Commerce of Mozambique
Nigeria
June 2019
Nigeria Association of Chambers of Commerce and Industry, Mines and Agriculture
Pakistan
October 2004
The Federation of Pakistan Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FPCCI)
Réunion
June 1995
Chambre of Commerce and d’Industrie de la Réunion
March 2002
L’Association pour le Développement Industriel de la Réunion
Russia
May 2007
Chamber of Commerce and Industry of the Russian Federation
Seychelles
November 2005
Seychelles Chamber of Commerce and Industry
April 2014
Seychelles Chamber of Commerce and Industry
Slovakia
September 2018
Slovak Chamber of Commerce and Industry (SCCI)
South Africa
September 2016
South African Chamber of Commerce and Industry
Sri Lanka
May 2004
National Chamber of Commerce of Sri Lanka
Taiwan
September 2017
Taiwan External Trade Development Council
Tanzania
January 2011
The Tanzania Chamber of Commerce, Industry and Agriculture (TCCIA)
Thailand
August 2004
The Federation of Thai Industries (F.T.I)
February 2013
TUSKON
Turkey
August 2014
DEIK (Foreign Economic Relations Board)
TOBB (The Union of Chambers and Commodity Exchanges of Turkey)